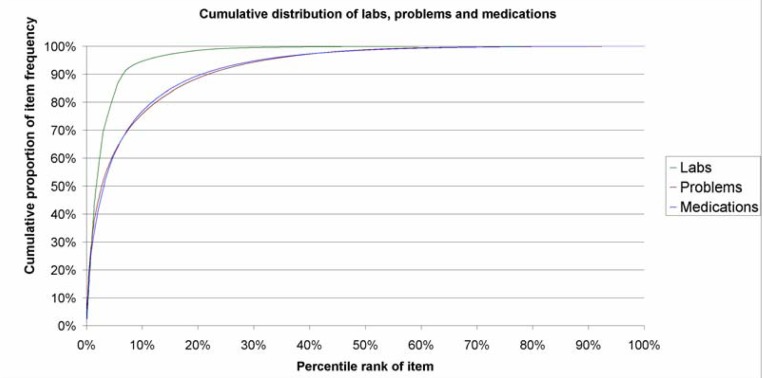
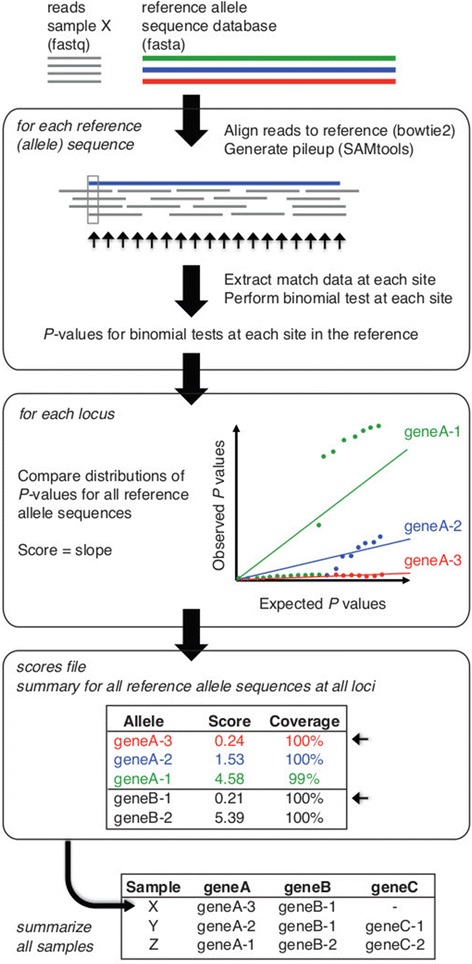
New technologies are an necessary means of addressing world health challenges and human growth. However, the street for new technologies from “lab to village” is neither easy nor easy.
Until lately, there was no conceptual framework for analyzing and addressing the myriad forces and points concerned in moving health technologies from the lab to those that want them. Recently, primarily based on empirical analysis, we printed such a mannequin.
In this paper, we give attention to extending the mannequin right into a dashboard and study how this dashboard can be utilized to handle the data associated to the trail from lab to village.
The subsequent step can be for teams involved in world health, and even the general public by way of the Internet, to use the device to assist information technologies down this difficult path to enhance world health and foster human growth.
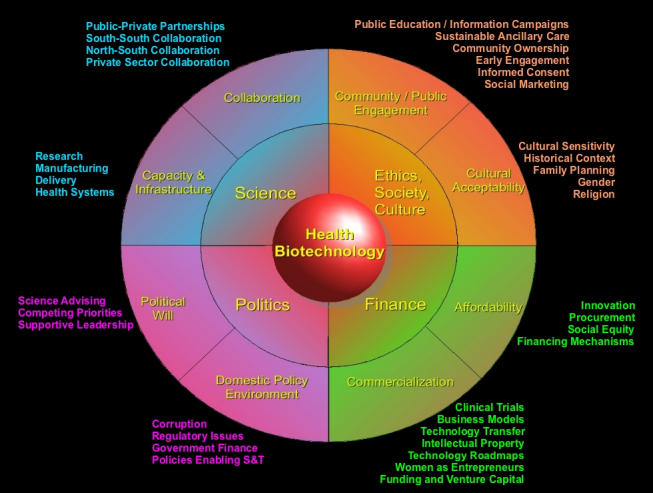
Lessons Learned From a Living Lab on the Broad Adoption of eHealth in Primary Health Care.
BACKGROUNDElectronic health (eHealth) options are thought-about to relieve present and future stress on the sustainability of main health care techniques. However, proof of the effectiveness of eHealth in each day apply is lacking.
Furthermore, eHealth options are sometimes not applied structurally after a pilot part, even when profitable throughout this part. Although many research on limitations and facilitators had been printed lately, eHealth implementation nonetheless progresses solely slowly.
To additional unravel the gradual implementation course of in main health care and speed up the implementation of eHealth, a 3-year Living Lab mission was arrange. In the Living Lab, referred to as eLabEL, sufferers, health care professionals, small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and analysis institutes collaborated to choose and combine totally mature eHealth technologies for implementation in main health care. Seven main health care facilities, 10 SMEs, and four analysis institutes participated.
OBJECTIVEThis viewpoint paper goals to present the method of adoption of eHealth in main care from the attitude of various stakeholders in a qualitative means. We present a real-world view on how such a course of happens, together with successes and failures associated to the totally different views.METHODSReflective and process-based notes from all conferences of the mission companions, interview knowledge, and knowledge of focus teams had been analyzed systematically utilizing 4 theoretical fashions to research the adoption of eHealth in main care.
RESULTSThe outcomes confirmed that large-scale implementation of eHealth depends upon the efforts of and interplay and collaboration amongst four teams of stakeholders: sufferers, health care professionals, SMEs, and people accountable for health care coverage (health care insurers and coverage makers).
These stakeholders are all performing inside their very own contexts and with their very own values and expectations.
We skilled that sufferers reported anticipated advantages relating to using eHealth for self-management functions, and health care professionals harassed the potential advantages of eHealth and had been involved in utilizing eHealth to distinguish themselves from different care organizations.
In addition, eHealth entrepreneurs valued the collaboration amongst SMEs as they weren’t large enough to enter the health care market on their very own and valued the collaboration with analysis institutes. Furthermore, health care insurers and coverage makers shared the ambition and wish for the event and implementation of an built-in eHealth infrastructure.
CONCLUSIONSFor optimum and sustainable use of eHealth, sufferers needs to be actively concerned, main health care professionals want to be strengthened of their administration, entrepreneurs ought to work intently with health care professionals and sufferers, and the federal government wants to give attention to new health care fashions stimulating improvements.
Only when all these events act collectively, beginning in native communities with a small vary of eHealth instruments, the potential of eHealth can be enforced.